Dot Fire Extinguisher Regulations A Comprehensive Guide

Dot fire extinguisher regulations are crucial for safety and compliance. This guide breaks down the essential aspects of DOT fire extinguisher regulations, from understanding the different types of extinguishers and their proper placement to mastering maintenance, labeling, transportation, and the consequences of non-compliance. We’ll cover everything you need to know to ensure your fire extinguishers meet DOT standards and keep you safe.
Understanding DOT fire extinguisher regulations isn’t just about avoiding fines; it’s about ensuring your safety and that of others. Properly maintained and strategically placed extinguishers can be the difference between a minor incident and a major disaster. This guide will help you navigate the complexities of these regulations, providing clear explanations and practical advice to help you stay compliant and prepared.
Types of DOT Fire Extinguishers

Source: fire-safe-au.com
DOT (Department of Transportation) regulations govern the types of fire extinguishers allowed for use in vehicles and other transport contexts. Understanding these regulations and the different extinguisher types is crucial for safety and compliance. Choosing the right extinguisher depends on the potential fire hazards you might encounter.
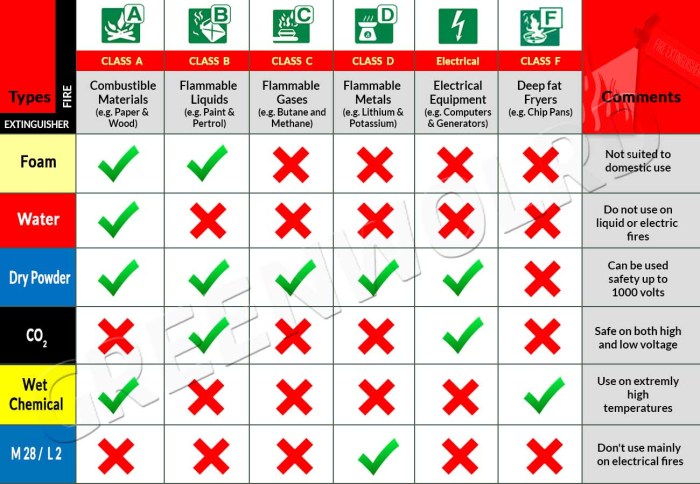
DOT Fire Extinguisher Classes and Applications
The types of fires categorize DOT-approved fire extinguishers they’re effective against. These classes are represented by letters, each indicating a specific class of flammable material. Misusing an extinguisher can be ineffective and even dangerous. Always select an extinguisher appropriate for the type of fire you are facing.
Extinguishing Agents in DOT-Approved Extinguishers
Depending on the class of fire, different extinguishing agents are used, different extinguishing agents are used. These agents work by interrupting the fire triangle (fuel, heat, oxygen), either removing the fuel source, reducing the heat, or displacing the oxygen. The choice of agent impacts the extinguisher’s effectiveness, weight, and potential environmental impact.
Comparison of DOT Fire Extinguisher Types
The table below compares common types of DOT-approved fire extinguishers. Note that specific weights and capacities can vary slightly depending on the manufacturer. Always check the extinguisher’s label for exact specifications.
| Extinguisher Type | Extinguishing Agent | Weight (approx.) | Capacity (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Water, Water with Additives | 5-10 lbs | 2.5-5 gallons |
| Class B | Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Dry Chemical (ABC or BC) | 5-20 lbs | 2-10 lbs |
| Class C | Carbon Dioxide (CO2), Dry Chemical (ABC or BC) | 5-20 lbs | 2-10 lbs |
| Class D | Dry Powder (specific to metal type) | Variable | Variable |
| Class K | Wet Chemical | Variable | Variable |
| Multi-Purpose (ABC) | Dry Chemical | 5-10 lbs | 2-10 lbs |
DOT Regulations for Fire Extinguisher Placement

Source: arescuer.com
Proper placement of fire extinguishers in vehicles is crucial for safety and compliance with Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations. Incorrect placement can hinder quick access in an emergency, potentially leading to more severe damage or injury. These regulations aim to ensure that fire extinguishers are readily available for use, minimizing response time and maximizing the chances of effectively controlling a fire.
DOT regulations don’t prescribe a single, universally applicable location for fire extinguishers in all vehicles. Instead, the placement must ensure easy and rapid access by the driver or other occupants without obstructing the safe operation of the vehicle. This consideration varies depending on the size and type of vehicle, and the number of extinguishers carried. The key is accessibility and avoiding any interference with critical vehicle controls or passenger movement.
Factors Influencing Fire Extinguisher Placement
Several factors influence where a fire extinguisher should be placed. These include the type of vehicle (e.g., passenger car, bus, truck), the size and weight of the extinguisher, the number of extinguishers carried, and the presence of other safety equipment. The extinguisher must be securely mounted to prevent it from shifting during vehicle operation and causing damage or injury. Furthermore, the placement must not interfere with the driver’s field of vision or impede access to critical vehicle controls such as the steering wheel, pedals, or gear shift.
Examples of Appropriate and Inappropriate Placement
To illustrate appropriate and inappropriate placement, consider a visual representation.
Panel A: Appropriate Placement
This panel shows three different vehicle types: a passenger car, a small delivery truck, and a large semi-truck.
* Passenger Car: The fire extinguisher is mounted securely under the driver’s seat, readily accessible but not obstructing legroom or pedals.
* Small Delivery Truck: The extinguisher is mounted on the driver’s side, within easy reach but not blocking access to the driver’s door or any controls. It is secured with a bracket to prevent shifting.
* Large Semi-Truck: The extinguisher is mounted in a designated area within the cab, easily accessible to the driver, but not obstructing the driver’s view or access to critical controls. Multiple extinguishers might be strategically located, possibly in the sleeper berth area as well, depending on the size and layout of the truck.
Panel B: Inappropriate Placement
This panel contrasts with Panel A, showing examples of poor placement.
* Passenger Car: The extinguisher is placed in the trunk, making it inaccessible in an emergency situation.
* Small Delivery Truck: The extinguisher is loosely placed on the floor behind the passenger seat, posing a risk of it shifting and becoming a projectile in a collision.
* Large Semi-Truck: The extinguisher is located in a difficult-to-reach area, such as behind a large stack of cargo, rendering it practically unusable in an emergency.
This visual comparison highlights the importance of considering accessibility and safety when choosing a location for fire extinguishers. Placement should prioritize quick access in emergencies while ensuring the extinguisher remains secure and doesn’t interfere with safe vehicle operation. Remember that local and state regulations may add further requirements beyond federal DOT guidelines.
DOT Regulations for Fire Extinguisher Maintenance and Inspection
Keeping your DOT-approved fire extinguishers in top shape isn’t just a good idea; it’s a legal requirement. Regular inspections and maintenance are crucial for ensuring they’ll work when you need them most, protecting lives and property. Neglecting this responsibility can lead to serious consequences, both legally and practically. This section details the procedures and importance of proper fire extinguisher care.
Regular inspection and maintenance of your DOT-approved fire extinguishers are vital for ensuring their effectiveness in an emergency. These procedures help identify potential problems before they become major issues, preventing equipment failure when you need it most. Furthermore, adhering to these regulations is crucial for compliance with DOT rules and avoiding potential penalties. Failure to maintain your extinguishers could result in hefty fines and even legal repercussions in the event of an accident or incident where a malfunctioning extinguisher contributed to a worse outcome.
DOT Fire Extinguisher Inspection Procedures
Regular inspections are key to ensuring your fire extinguishers are ready for action. A simple visual check can often catch small problems before they escalate. More thorough inspections, including a pressure check, should be performed periodically by a qualified technician. Remember, a malfunctioning extinguisher is worse than no extinguisher at all.
- Visual Inspection (Monthly): Check for any visible damage, corrosion, dents, or leaks. Look at the gauge to ensure the pressure is within the acceptable range. Examine the hose and nozzle for any cracks or obstructions. Verify that the safety pin is in place and the extinguisher is easily accessible.
- Detailed Inspection (Annually): This more thorough inspection should be carried out by a qualified technician. It includes a complete visual inspection as above, plus a pressure test to ensure the extinguisher is properly charged and ready for use. The technician will also check for internal corrosion and other potential issues not visible during a simple visual check.
- Hydrostatic Testing (Periodic): Depending on the type of extinguisher and its age, hydrostatic testing may be required. This involves a pressure test far exceeding the operating pressure to check for structural integrity. The frequency of this test is usually specified by the manufacturer and is crucial for ensuring the extinguisher’s long-term reliability.
Consequences of Neglecting Fire Extinguisher Maintenance
Ignoring the maintenance requirements for your DOT-approved fire extinguishers can have severe consequences. At best, you’ll have a useless piece of equipment during an emergency. At worst, a malfunctioning extinguisher could lead to a more significant incident or even injury. Compliance with DOT regulations is not just a suggestion; it’s a necessity for safety and legal reasons.
- Fines and Penalties: Non-compliance with DOT regulations regarding fire extinguisher maintenance can result in substantial fines and penalties. The exact amounts vary depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction.
- Increased Risk of Injury or Property Damage: A malfunctioning extinguisher during a fire could lead to more extensive damage and potential injuries due to the inability to control the fire effectively. This could result in increased insurance premiums and legal liabilities.
- Legal Liability: In the event of an accident or incident, failure to properly maintain fire extinguishers could be used against you in a legal case. This could result in significant financial losses and reputational damage.
DOT Fire Extinguisher Inspection Checklist
This checklist provides a quick reference for conducting a thorough inspection of your DOT fire extinguisher. Remember, regular and careful inspections are vital for ensuring the safety and functionality of your equipment. Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions for specific recommendations.
- Is the extinguisher easily accessible and visible?
- Is the extinguisher free from any visible damage (dents, corrosion, leaks)?
- Is the safety pin in place and secured?
- Is the pressure gauge within the acceptable range (check manufacturer’s specifications)?
- Is the nozzle and hose free from obstructions and damage?
- Are the instructions and labels legible and visible?
- Has the extinguisher been serviced and inspected according to the manufacturer’s recommendations?
- Has the extinguisher undergone hydrostatic testing as required?
DOT Fire Extinguisher Labeling and Marking Requirements: Dot Fire Extinguisher Regulations
Source: jimcdn.com
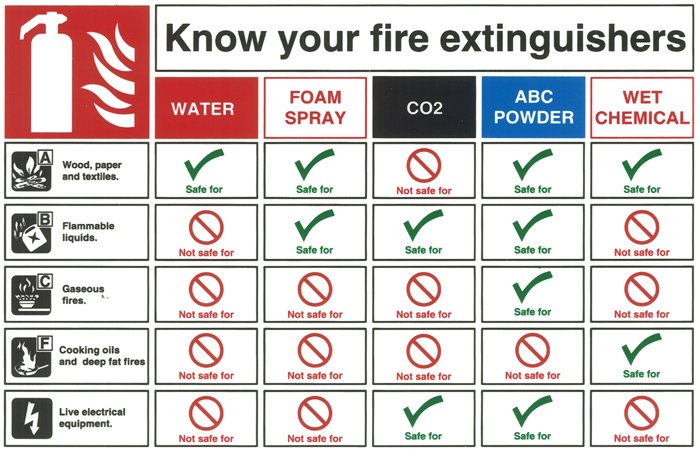
Proper labeling and marking of DOT-approved fire extinguishers are crucial for safety and efficient emergency response. Clear and easily understood markings ensure that firefighters and other responders can quickly identify the type and capacity of the extinguisher, enabling them to effectively combat a fire. Ambiguous or missing markings can lead to delays and potentially hinder successful fire suppression efforts.
DOT regulations mandate specific labeling and marking requirements to ensure consistency and clarity. These requirements cover the extinguisher’s type, capacity, operating instructions, and manufacturer information. Legible markings are vital for quick identification under stressful emergency conditions when time is of the essence.
Extinguisher Type and Capacity Marking
The type of extinguishing agent and the capacity of the extinguisher must be carked. This information is critical for responders to select the appropriate extinguisher for the specific type of fire. For example, a Class B extinguisher is designed for flammable liquid fires, while a Class A extinguisher is for ordinary combustibles. The capacity, usually expressed in pounds or kilograms, indicates the amount of extinguishing agent available. This helps responders assess whether the extinguisher is sufficient for the size of the fire.
Operating Instructions Marking
Clear and concise operating instructions are essential. These instructions should be easily visible and understandable, even under duress. They typically involve a simple sequence of steps: AIM, SQUEEZE, SWEEP. The instructions should also include any specific safety precautions associated with the extinguisher type.
Manufacturer Information Marking
The manufacturer’s name, address, and possibly a model number should be permanently marked on the extinguisher. This information aids in traceability and facilitates contacting the manufacturer for any queries or warranty claims.
Sample Label and Marking
Extinguisher Type: ABC
Capacity: 10 lbs (4.5 kg)
Manufacturer: Acme Fire Safety, Inc. 123 Main St, Anytown, USA
Operating Instructions: AIM at the base of the fire. SQUEEZE the lever. SWEEP from side to side.
WARNING: Do not use on energized electrical equipment.
Extinguisher Type: CO2
Capacity: 5 lbs (2.3 kg)
Manufacturer: Beta Fire Protection, 456 Oak Ave, Cityville, USA
Operating Instructions: AIM nozzle at the base of the fire. SQUEEZE the lever. SWEEP from side to side. Keep a safe distance from the discharge.
WARNING: May cause frostbite on contact.
DOT Regulations for Fire Extinguisher Transportation
Safe transportation of DOT-approved fire extinguishers is crucial to prevent accidents and injuries. Improper handling can lead to leaks, damage, or even explosions, posing significant risks to both the transporter and the surrounding environment. These regulations cover both the movement of extinguishers within vehicles and during larger shipments.
Proper transportation of fire extinguishers involves adhering to specific guidelines depending on the extinguisher type and mode of transport. Failure to do so can result in penalties and, more importantly, serious safety hazards. Understanding these regulations is key to ensuring safe and compliant transport.
Regulations for Transporting Fire Extinguishers Within Vehicles, Dot fire extinguisher regulations
Transporting fire extinguishers in vehicles requires securing them to prevent movement during transit. This is vital to avoid damage to the extinguisher and potential harm to vehicle occupants in the event of an accident. The extinguisher must be securely mounted, often using brackets or straps, to prevent it from shifting or falling. The mounting location should also consider accessibility for use in case of emergency, but prioritize safety during transit. For example, a fire extinguisher should not be placed where it could obstruct the driver’s view or impede airbag deployment. Additionally, the extinguisher should be protected from damage by being positioned away from sharp objects or areas prone to impact.
Regulations for Transporting Fire Extinguishers During Shipment
Shipping fire extinguishers involves additional considerations beyond those for in-vehicle transport. Larger shipments necessitate proper packaging to protect the extinguishers from damage during handling and transit. This often includes using sturdy containers with appropriate cushioning materials to absorb shocks and vibrations. Furthermore, the packaging must display hazard labels indicating the contents and any necessary handling precautions. The shipping documentation must also accurately reflect the contents, including the type and quantity of fire extinguishers being shipped, adhering to all relevant DOT hazardous materials regulations.
Potential Hazards Associated with Improper Transportation
Improper transportation of fire extinguishers presents several significant hazards. Loose or unsecured extinguishers can become projectiles in a collision, causing injury or damage. Damage to the extinguisher itself can lead to leaks, releasing the extinguishing agent and potentially causing environmental harm or rendering the extinguisher ineffective. In some cases, damage could even result in an accidental discharge, leading to further hazards. For example, a damaged extinguisher containing a pressurized agent could rupture, causing injury from the released pressure and agent. Improper labeling or documentation can lead to delays, fines, and potential safety issues for those handling the shipment.
Comparison of Regulations for Different Fire Extinguisher Types
Regulations for transporting different types of DOT-approved fire extinguishers may vary slightly based on the extinguishing agent used. For instance, extinguishers containing halon or other ozone-depleting substances are subject to stricter regulations due to environmental concerns. Extinguishers containing flammable or corrosive agents may require additional safety precautions during transport, including specialized packaging and handling procedures. These differences are usually detailed in the specific DOT regulations and associated shipping documentation. For example, a dry chemical extinguisher might have different packaging requirements compared to a CO2 extinguisher due to differences in the agent’s properties.
Compliance and Penalties for Non-Compliance
Staying compliant with DOT fire extinguisher regulations is crucial for safety and avoiding hefty fines. Non-compliance can lead to significant consequences, impacting your operations and potentially causing harm. Understanding the penalties and reporting procedures is essential for the responsible handling of fire extinguishers in transportation.
Penalties for non-compliance with DOT fire extinguisher regulations vary depending on the severity and nature of the violation. These can range from warnings and administrative fines to significant financial penalties and even legal action. The specific penalties are determined by the regulatory body overseeing the transportation, which is usually the Department of Transportation (DOT) or a similar agency in other countries. Factors considered include the type of violation, the potential risk to safety, and the history of compliance of the involved party. For example, a minor infraction like an improperly placed extinguisher might result in a warning, while a failure to maintain or inspect extinguishers leading to a fire could result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Penalties for Non-Compliance with DOT Fire Extinguisher Regulations
The potential penalties for non-compliance are substantial and can significantly impact businesses. These penalties are designed to incentivize compliance and ensure the safety of transportation. They serve as a deterrent against negligence and encourage proactive maintenance and responsible handling of fire extinguishers. For example, a trucking company failing to properly maintain its fire extinguishers could face thousands of dollars in fines per violation, along with potential legal action if a fire results from this negligence. Furthermore, repeated violations can lead to increased penalties and the suspension or revocation of operating licenses.
Reporting Non-Compliant Fire Extinguishers
Reporting non-compliant fire extinguishers is a crucial step in ensuring safety and compliance. If you encounter a fire extinguisher that appears to be damaged, improperly maintained, or otherwise non-compliant with DOT regulations, it’s vital to report it immediately. The reporting process typically involves contacting the relevant regulatory authority, such as the DOT, or the company responsible for the extinguisher’s maintenance. The report should include details about the extinguisher’s location, condition, and any identifying information. Prompt reporting allows for swift action to address the issue, preventing potential hazards and ensuring compliance. Failure to report a non-compliant extinguisher could result in penalties if a subsequent incident occurs due to the neglected extinguisher.
Obtaining Certifications and Approvals for DOT Fire Extinguishers
Obtaining necessary certifications and approvals for DOT fire extinguishers is a critical aspect of compliance. These certifications ensure that the extinguishers meet the required safety standards and are suitable for transportation. The process generally involves obtaining certification from a recognized testing and certification body that confirms the extinguisher meets the specified DOT standards. This certification typically includes documentation verifying the extinguisher’s design, construction, performance, and testing results. Companies that manufacture or distribute DOT fire extinguishers are responsible for obtaining these certifications and providing documentation to customers. These certifications are crucial for demonstrating compliance during inspections and audits.
Wrap-Up
Source: co. in
Staying compliant with DOT fire extinguisher regulations is a straightforward process when you understand the rules. By following the guidelines on extinguisher types, placement, maintenance, labeling, and transportation, you can significantly reduce risks and ensure your compliance. Remember, proactive maintenance and regular inspections are key to keeping your fire extinguishers ready for action. Prioritizing safety and adhering to these regulations protects lives and property. This guide serves as a starting point; always refer to the official DOT regulations for the most up-to-date information.
General Inquiries
What are the common causes of fire extinguisher failure?
Common causes include corrosion, leaks, improper storage (extreme temperatures or humidity), and lack of regular maintenance/inspection.
How often should I have my DOT fire extinguishers inspected?
The frequency varies depending on the type of extinguisher and your specific industry, but annual inspections are generally recommended.
What should I do if I find a non-compliant fire extinguisher?
Immediately remove it from service, tag it as non-compliant, and contact a qualified service technician for repair or replacement. Report it according to your company’s procedures and potentially to relevant authorities depending on the severity.
Can I use any type of fire extinguisher in my vehicle?
No, only DOT-approved extinguishers are allowed in vehicles subject to DOT regulations. The type of extinguisher should be appropriate for the potential fire hazards in your vehicle.
What are the penalties for non-compliance with DOT fire extinguisher regulations?
Penalties can range from warnings and fines to vehicle impoundment, depending on the severity of the violation and the jurisdiction. Consult the official DOT regulations for specifics.
Comments are closed.