Cost For New House Siding A Complete Guide
Cost for new house siding? It’s a big decision, and knowing the costs upfront can save you headaches (and money!). This guide breaks down everything you need to know, from choosing the right material to finding a reliable contractor. We’ll explore different siding types, their costs, and the factors influencing the overall price. Get ready to become a siding expert!
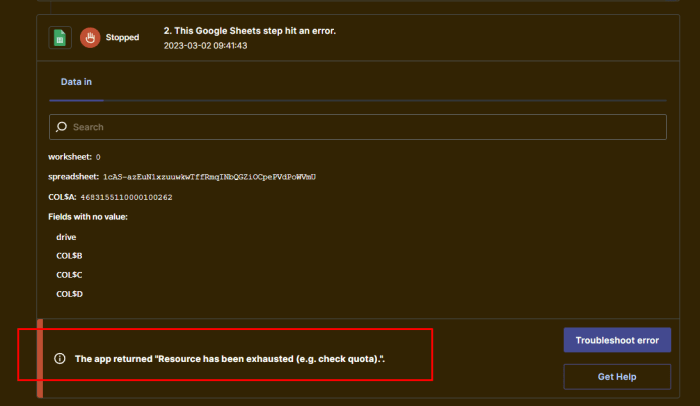
We’ll cover the various siding materials available – vinyl, wood, fiber cement, and metal – comparing their costs, pros, and cons. We’ll also look at how factors like your home’s size, location, and the complexity of the installation affect the final price. Budgeting and financing options will be explored, along with tips for finding the right contractor and maintaining your new siding.
Types of House Siding Materials
Choosing the right siding for your house is a big decision, that impacts both the aesthetics and the longevity of your home. This section will break down the most common siding materials, comparing their costs, lifespans, maintenance needs, and visual appeal to help you make an informed choice.
Siding Material Comparison
The following table provides a comparison of common siding materials, considering cost, pros, and cons. Remember that prices can vary significantly based on location, material quality, and labor costs. These figures are estimates and should be considered as a starting point for your budgeting.
| Material | Cost per Square Foot | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vinyl | $3-$12 | Low maintenance, affordable, wide variety of colors and styles, durable | Can fade over time, susceptible to damage from impact, and may not be as aesthetically pleasing as other options to some |
| Wood | $7-$25+ | Classic look can be painted or stained, relatively easy to repair | High maintenance (painting, staining, sealing), susceptible to rot, insect infestation, and fire damage, relatively expensive |
| Fiber Cement | $8-$15+ | Durable, fire-resistant, and low maintenance, can mimic the look of wood | More expensive than vinyl, can be brittle and prone to cracking if not installed properly, heavier than other options, requires professional installation |
| Metal | $10-$20+ | Extremely durable, long lifespan, fire-resistant, low maintenance, energy efficient | Can dent, is susceptible to scratches, can be noisy in rain or hail, expensive, limited color options compared to vinyl. |
Lifespan and Maintenance
The lifespan and maintenance requirements of siding materials vary considerably. Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years with minimal maintenance, requiring occasional cleaning. Wood siding, depending on the type and quality, might last 20-50 years but needs regular painting, staining, and sealing to prevent rot and insect damage. Fiber cement siding boasts a lifespan of 50 years or more with relatively low maintenance, needing only periodic cleaning. Metal siding is the longest-lasting option, often lasting 50 years or more with minimal maintenance.
Aesthetic Appeal
The aesthetic appeal of siding is subjective, but each material offers a distinct look and feel. Vinyl siding offers a wide range of colors and styles, from traditional clapboard to more modern designs. However, it often lacks the depth and texture of other materials. Wood siding provides a classic, warm look with a natural texture and a wide variety of color options through staining and painting. Fiber cement siding can mimic the look of wood, offering a similar texture and aesthetic, but with greater durability. Metal siding often has a more modern, sleek appearance with a smooth, flat texture and a limited range of colors, typically muted earth tones or metallic shades. For instance, a traditional colonial home might look best with wood siding, whereas a modern farmhouse could be enhanced by fiber cement or metal siding, while vinyl would suit a variety of styles. Consider your home’s architectural style and your personal preferences when choosing a material.
Factors Affecting Siding Cost

Source: insided.com
Getting new siding is a big investment, and the final price tag depends on a lot more than just the type of material you choose. Several factors work together to determine the overall cost, and understanding these can help you budget effectively. Let’s break down the key influences.
The total cost of your siding project is a combination of material costs, labor costs, and the complexity of the job itself. Material costs vary widely depending on the type of siding (as discussed previously), its quality, and the amount needed. Labor costs are influenced by factors like the contractor’s experience, location, and the time required for installation. Finally, the complexity of the project, such as the shape of your house, the presence of intricate details, or the need for extensive repairs before installation, significantly impacts both labor and material costs.
Geographic Location and Siding Prices
Regional differences significantly impact siding costs. Labor rates for skilled tradespeople, like siding installers, vary widely across the country. Areas with high costs of living, such as major metropolitan areas on either coast, generally have higher labor rates compared to more rural areas in the Midwest or South. Furthermore, material transportation costs and local supply and demand also play a role. For example, cedar siding might be cheaper in regions with abundant cedar forests, while vinyl siding prices could be influenced by manufacturing locations and shipping distances. A hypothetical comparison: installing the same type and amount of vinyl siding on a similar-sized house could cost $10,000 in a rural area of the Midwest but $15,000 in a major city like New York or Los Angeles, due primarily to labor costs and material transportation.
House Size and Installation Difficulty
The size of your house directly correlates with the amount of siding needed and, consequently, the material costs. A larger house naturally requires more siding, increasing the overall expense. Beyond sheer size, the complexity of your home’s exterior also plays a crucial role. A house with many angles, dormers, or intricate architectural details will require more time and skill from the installers, leading to higher labor costs. For instance, installing siding on a simple ranch-style house will be quicker and less expensive than on a Victorian-style home with numerous gables, turrets, and decorative trim. Consider a scenario: siding a 1,500 sq ft ranch-style house might cost $8,000-$12,000 while siding a 2,500 sq ft Victorian-style house with complex details could easily cost $15,000-$25,000 or more.
Siding Installation Process
Getting new siding is a big project, and understanding the installation process will help you manage expectations and communicate effectively with your contractor. This involves several key steps, from preparation to final cleanup. A well-executed installation ensures both the longevity and aesthetic appeal of your new siding.
The siding installation process is a multi-stage undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Each stage is crucial for a successful outcome, impacting both the final look and the lifespan of your new siding. Proper preparation and adherence to building codes are essential for a quality installation.
Permitting and Inspections
Building permits are almost always required for exterior home renovations like siding installation. These permits ensure the work complies with local building codes and safety regulations. The application process typically involves submitting plans and specifications to your local building department. Inspections are scheduled at various stages of the project—often before, during, and after installation—to verify compliance. Failing to obtain necessary permits can result in fines and even force the removal of the newly installed siding. Inspections ensure the work meets safety standards and that the installation is structurally sound. For example, an inspector might check for proper flashing around windows and doors to prevent water damage.
Siding Installation Stages
The actual installation process itself varies slightly depending on the type of siding used, but generally follows these steps:
- Preparation: This initial phase involves removing the old siding, repairing any underlying sheathing or wall damage, and installing house wrap (a water-resistant barrier) to protect the home’s structure. Proper preparation is vital to prevent future problems and ensure the longevity of the new siding.
- Framing and Flashing: New framing may be necessary to accommodate different siding thicknesses or to address any structural issues. Flashing, a thin metal strip, is installed around windows, doors, and other openings to prevent water intrusion. This is a crucial step for preventing water damage.
- Siding Installation: This is where the actual siding goes on. The method varies depending on the type of siding (we’ll discuss this further below). Careful attention to detail, such as proper overlapping and securing, is crucial for a watertight and aesthetically pleasing finish. For example, vinyl siding is typically nailed directly to the sheathing, while fiber cement may require more complex fastening techniques.
- Finishing Touches: This involves installing trim, soffit, and fascia boards to complete the exterior look. Caulking and sealing any gaps are vital to prevent drafts and water damage. This stage significantly impacts the overall aesthetic appeal and weather protection.
- Cleanup: Finally, all debris and leftover materials are removed from the property, leaving a clean and finished project. Professional contractors typically handle this step efficiently.
Siding Installation Methods and Cost Implications
Different siding types necessitate different installation methods, which directly impact the overall cost. The complexity of the installation process often determines labor costs.
| Siding Type | Installation Method | Cost Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Vinyl Siding | Nailed directly to sheathing; relatively straightforward | Generally lower installation cost due to simplicity |
| Fiber Cement Siding | Requires more precise cutting and fastening; may need specialized tools | Higher installation cost due to increased labor and material requirements |
| Wood Siding | Can be nailed or screwed; requires careful attention to sealing and finishing | Installation cost varies greatly depending on wood type and finish |
| Metal Siding | Often involves specialized tools and techniques; requires precision | Installation ccostscan be moderate to high depending on the type of metal and complexity of the design |
Budgeting and Financing Options: Cost For New House Siding
Replacing your house siding is a significant investment, so careful budgeting and planning are crucial. Understanding the costs involved and exploring various financing options will help you manage the project effectively and avoid unexpected financial strain. This section will guide you through creating a realistic budget and exploring different ways to finance your siding replacement.
Sample Siding Replacement Budget
Creating a detailed budget is the first step. This ensures you have a clear picture of the total cost before you begin. The following table provides a sample budget; remember that your actual costs may vary depending on your home’s size, location, and chosen materials.
| Budget Item | Estimated Cost | Notes | Contingency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials (Siding, Trim, Flashing) | $8,000 – $15,000 | Cost varies greatly depending on material choice (vinyl, wood, fiber cement, etc.) and square footage. | $1,000 |
| Labor | $5,000 – $10,000 | Labor costs depend on the complexity of the job and the contractor’s rates. | $1,500 |
| Permits | $300 – $800 | Permit fees vary by location and project scope. | $200 |
| Waste Removal | $200 – $500 | Cost depends on the amount of waste generated. | $100 |
| Total Estimated Cost | $13,500 – $26,300 | $2,800 |
Note: The contingency is 20% of the total estimated cost to account for unexpected expenses.
Financing Options for Siding Replacement
Several financing options are available for home improvement projects like siding replacement. Each has its advantages and disadvantages.
Here are a few common options:
- Home Equity Loan: This loan uses your home’s equity as collateral. Pros: Lower interest rates than personal loans. Cons: Risks foreclosure if you default. Requires sufficient equity in your home.
- Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC): Similar to a home equity loan, you can borrow money as needed up to a certain limit. Pros: Flexibility in borrowing. Cons: Interest rates can be variable, leading to unpredictable payments. Requires sufficient equity.
- Personal Loan: A loan from a bank or credit union, not secured by your home. Pros: Easier to qualify for than home equity loans. Cons: Higher interest rates.
- Credit Card: Using a credit card offers convenience but is generally the least favorable option due to high interest rates and the potential for debt accumulation. Only consider this if you can pay off the balance quickly.
- Contractor Financing: Some contractors offer financing options directly. Pros: Can simplify the process. Cons: Interest rates may be higher than other options. Always compare rates.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI) for Siding
A siding upgrade can increase your home’s value and curb appeal. Calculating the ROI helps determine if the investment is worthwhile.
Here’s how to calculate ROI:
ROI = (Increase in Home Value – Total Project Cost) / Total Project Cost * 100%
Example:
Let’s say your siding replacement costs $15,000. After the upgrade, a real estate appraisal shows your home’s value increased by $20,000.
ROI = ($20,000 – $15,000) / $15,000 * 100% = 33.33%
This means you have a 33.33% return on your investment. However, this is a simplified calculation. Factors like market conditions and the type of siding can affect the actual ROI.
Finding and Hiring Contractors
Finding the right contractor for your new siding is crucial for a successful project. A reputable contractor will not only deliver high-quality work but also manage the project efficiently and within budget. Choosing the wrong contractor, however, can lead to costly mistakes, delays, and significant headaches. This section will guide you through the process of finding and hiring a qualified siding professional.
Choosing a contractor involves more than just checking their license and insurance. You need to evaluate their experience, reputation, and communication skills to ensure a smooth and successful project. Remember, this is a significant investment, so taking your time to find the right fit is worthwhile.
Contractor Selection Criteria, Cost for new house siding
Before you start contacting contractors, it’s helpful to have a clear understanding of what you’re looking for. This includes the type of siding, your budget, and your project timeline. With this information in hand, you can begin your search. Start by asking friends, family, and neighbors for recommendations. Online reviews on sites like Yelp, Angie’s List, and HomeAdvisor can also provide valuable insights into a contractor’s reputation and work quality. Check the Better Business Bureau (BBB) website for any complaints or negative reviews. Look for contractors with extensive experience in installing the specific type of siding you’ve chosen.
Questions to Ask Potential Contractors
It’s essential to ask prospective contractors a series of questions to assess their qualifications and suitability for your project. Thorough questioning will help you avoid potential problems and ensure you choose a reliable and competent professional. Don’t hesitate to ask detailed questions; it’s your home and investment.
- How long have you been in business, and what is your experience with [Specific Siding Type] installation?
- Can you provide references from past clients, including contact information?
- Are you licensed and insured? What is the coverage amount of your liability insurance and workers’ compensation insurance?
- What is your process for handling unforeseen issues or changes during the project?
- Can you provide a detailed, itemized estimate, including materials, labor, and any permits?
- What is your payment schedule, and what are your policies regarding change orders?
- What is your warranty on materials and workmanship?
- Do you have a portfolio of completed projects that I can review?
- What is your timeline for completing the project, and what is your contingency plan for delays?
- How will you protect my property during the installation process?
The Importance of Multiple Quotes
Getting multiple quotes from different contractors is crucial for comparing prices and services. This process allows you to identify the best value for your money and ensure you are not overpaying. Don’t solely focus on the lowest price; consider the contractor’s experience, reputation, and the overall value they offer. Comparing quotes will highlight variations in materials, labor costs, and project timelines, allowing for a more informed decision. For example, one contractor might offer a lower initial price but use cheaper materials, potentially leading to higher maintenance costs in the long run. Another might have a longer project timeline, which could disrupt your schedule. By comparing multiple quotes, you can make a well-informed decision that aligns with your budget and priorities.
Maintenance and Repair of Siding
Source: githubusercontent.com
Proper siding maintenance is crucial for preserving your home’s curb appeal and protecting it from the elements. Neglecting maintenance can lead to costly repairs down the line, so a proactive approach is best. Regular cleaning and inspections will help identify minor issues before they escalate into major problems.
Regular maintenance extends the life of your siding, potentially saving you thousands of dollars in premature replacement costs. For example, a simple cleaning might prevent minor damage from becoming a full-blown repair job involving replacing multiple panels.
Common Siding Maintenance Tasks and Their Frequency
Regular maintenance involves several simple tasks that, when performed consistently, significantly extend the lifespan of your siding. These tasks are not overly time-consuming and can often be incorporated into other routine home maintenance activities.
- Annual Cleaning: Wash your siding with a garden hose and a soft-bristled brush, removing dirt, debris, and cobwebs. For stubborn stains, use a mild detergent solution. Avoid high-pressure washers, which can damage the siding.
- Semi-Annual Inspection: Inspect your siding twice a year (spring and fall) for signs of damage such as cracks, loose panels, or insect infestation. Pay close attention to areas prone to moisture damage, like corners and around windows and doors.
- Caulk Replacement (Every 2-3 Years): Check and replace caulking around windows, doors, and other areas where siding meets other building materials. Cracked or missing caulk can allow water to penetrate, leading to rot and damage.
- Painting or Staining (Every 5-10 Years): Depending on the type of siding and exposure to the elements, repainting or restaining may be necessary to maintain its appearance and protect it from UV damage. The frequency will vary greatly depending on the quality of the paint/stain and the climate.
Typical Siding Repair Procedures and Associated Costs
Repair costs vary greatly depending on the type of siding, the extent of the damage, and the cost of labor in your area. Simple repairs are often manageable as DIY projects, while more extensive repairs should be handled by a professional.
- Replacing a Single Damaged Panel: This might cost between $50 and $200, depending on the siding material and the cost of the replacement panel. Labor costs are typically included in this estimate.
- Repairing Minor Cracks: Small cracks can often be repaired with caulk or patching compound. The cost is usually minimal, involving only the cost of materials (a few dollars).
- Repairing Water Damage: Repairing water damage is more extensive and may involve replacing multiple panels or repairing underlying sheathing. The cost can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the severity of the damage.
- Insect Infestation Repair: Treating insect infestations may require pesticide treatment and possibly the replacement of damaged siding. Costs vary widely based on the extent of the infestation and the type of siding.
Signs Indicating the Need for Siding Repair or Replacement
Several warning signs indicate that your siding needs attention. Ignoring these signs can lead to more extensive and costly repairs down the road.
- Visible Cracks or Holes: Cracks, holes, or gaps in the siding allow water to penetrate, leading to rot and structural damage. These should be addressed immediately.
- Loose or Damaged Panels: Loose or damaged panels can be easily dislodged by wind or other weather events, compromising the integrity of your home’s exterior.
- Water Stains or Rot: Dark stains or signs of rot indicate water intrusion. This is a serious problem that requires prompt attention to prevent further damage.
- Extensive Peeling Paint or Stain: Extensive peeling paint or stain indicates that the siding is no longer adequately protected from the elements. This can lead to premature deterioration.
- Insect Infestation: Evidence of insect infestation, such as holes or tunnels in the siding, requires immediate attention to prevent further damage and structural compromise. A professional inspection is often recommended.
Final Summary
Source: sstatic.net
Replacing your house siding is a significant investment, but with careful planning and research, you can make informed decisions that fit your budget and enhance your home’s curb appeal. Remember to get multiple quotes, ask plenty of questions, and choose materials that align with your style and long-term goals. By understanding the costs involved and the process of installation, you can confidently embark on this home improvement project, transforming your house into the home of your dreams.
Question & Answer Hub
What’s the average lifespan of different siding materials?
Vinyl siding typically lasts 20-30 years, wood siding 20-50 years (depending on maintenance), fiber cement 50+ years, and metal siding 40-50 years.
Can I install the siding myself?
While possible for smaller projects, professional installation is generally recommended for a quality, long-lasting result. DIY can void warranties and potentially lead to costly mistakes.
How do I choose a reputable contractor?
Check online reviews, verify licenses and insurance, get multiple quotes, and ask for references. Look for contractors with experience in the type of siding you’ve chosen.
What are some common siding problems and how much do repairs cost?
Common issues include cracks, dents, rot (wood siding), and fading. Repair costs vary greatly depending on the extent of the damage and the type of siding. Small repairs might be relatively inexpensive, while larger problems could be costly.
What’s the best time of year to install new siding?
Spring and fall are generally ideal, as extreme temperatures can affect the installation process and the curing of some materials.
Comments are closed.